Chronic Stress Is Wrecking Your Health—Here’s How to Regain Control (Backed by Science)
Introduction:
Stress isn’t just “in your head.” It affects your body, hormones, gut, sleep, and even your ability to think clearly. While short bursts of stress are normal—even helpful—chronic stress is a silent disruptor that can slowly wear you down.
In this article, we explore the real science behind stress, how it impacts your health, and practical, research-backed ways to manage it—without needing to overhaul your life.
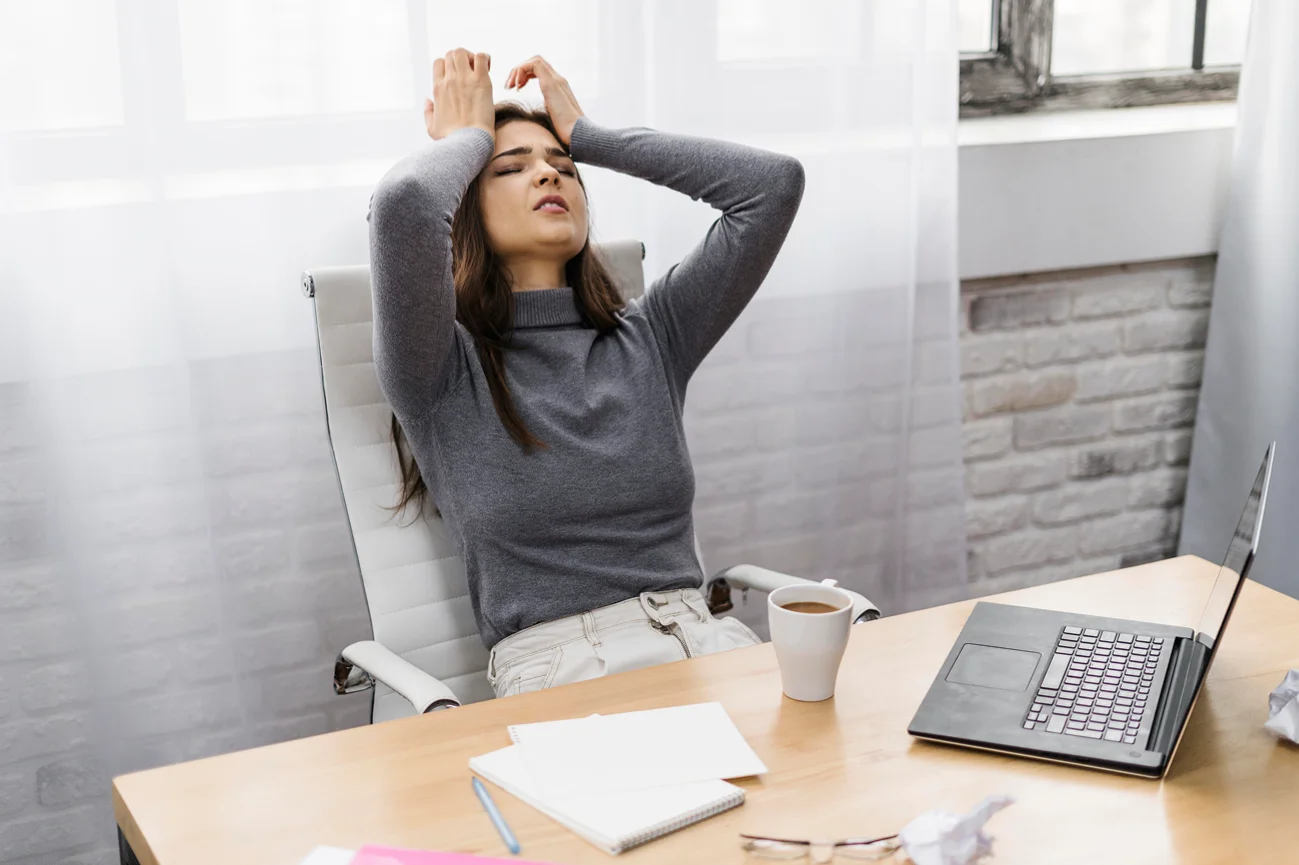

1. What Happens to Your Body When You’re Stressed?
When you're under stress, your body releases cortisol and adrenaline, hormones that prepare you for "fight or flight." But when stress becomes constant, those same hormones:
Raise blood pressure
Disrupt digestion
Suppress the immune system
Contribute to weight gain, especially around the belly
Interfere with sleep and memory
Long-term stress has even been linked to conditions like anxiety, depression, heart disease, and insulin resistance.
2. 5 Hidden Signs of Chronic Stress You Shouldn’t Ignore
Sometimes, we normalize stress so much that we miss the signals. Watch for:
Frequent headaches or muscle tension
Digestive issues like bloating or constipation
Mood swings, irritability, or feeling “numb”
Difficulty falling or staying asleep
Relying heavily on caffeine, sugar, or alcohol
These are your body’s way of waving a red flag.
3. Science-Backed Ways to Reduce Stress Naturally
You don’t need a weekend retreat—just a few consistent, low-effort strategies can make a big difference.
🌿 1. Practice Box Breathing
This Navy SEAL technique reduces anxiety and calms the nervous system.
Inhale for 4 seconds → Hold for 4 → Exhale for 4 → Hold for 4
Repeat for 1–2 minutes when you feel overwhelmed.
🌞 2. Get 10–20 Minutes of Daylight
Natural light, especially in the morning, helps reset your cortisol rhythm and boosts serotonin. This improves your mood and helps you sleep better at night.
✍️ 3. Use a “Brain Dump” Journal at Night
Writing down your thoughts before bed clears mental clutter and helps prevent overthinking. Even 5 minutes can reduce racing thoughts and improve sleep.
🧘♀️ 4. Move Gently Every Day
Walking, yoga, or stretching releases endorphins—the body’s natural stress relievers. It also reduces muscle tension caused by emotional strain.
🎧 5. Try “Binaural Beats” or Soothing Music
These sounds stimulate alpha brain waves, which are linked to calm focus. Many free apps or playlists can guide you.
4. Don’t Ignore the Gut-Brain Connection
Your gut and brain talk through the vagus nerve, and stress can disrupt this communication—leading to bloating, food sensitivity, or loss of appetite.
Support your gut with:
Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, or kefir
Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables
Deep breathing to activate the vagus nerve and promote digestion
5. Rethink How You Handle Your To-Do List
One overlooked source of stress is mental overload. Try:
Writing just 3 priorities per day
Using the Pomodoro technique (25 mins work, 5 mins rest)
Saying “no” to low-impact tasks that drain energy
You don’t need to do more—you need to focus on what matters.
Final Thoughts
Stress might be a part of modern life, but burnout doesn’t have to be. By making small, consistent adjustments to how you breathe, move, eat, and think, you can retrain your nervous system to feel calm—even when life gets messy.
Your peace isn’t a luxury—it’s a daily habit.
Start today with one small change. Your future self will thank you.





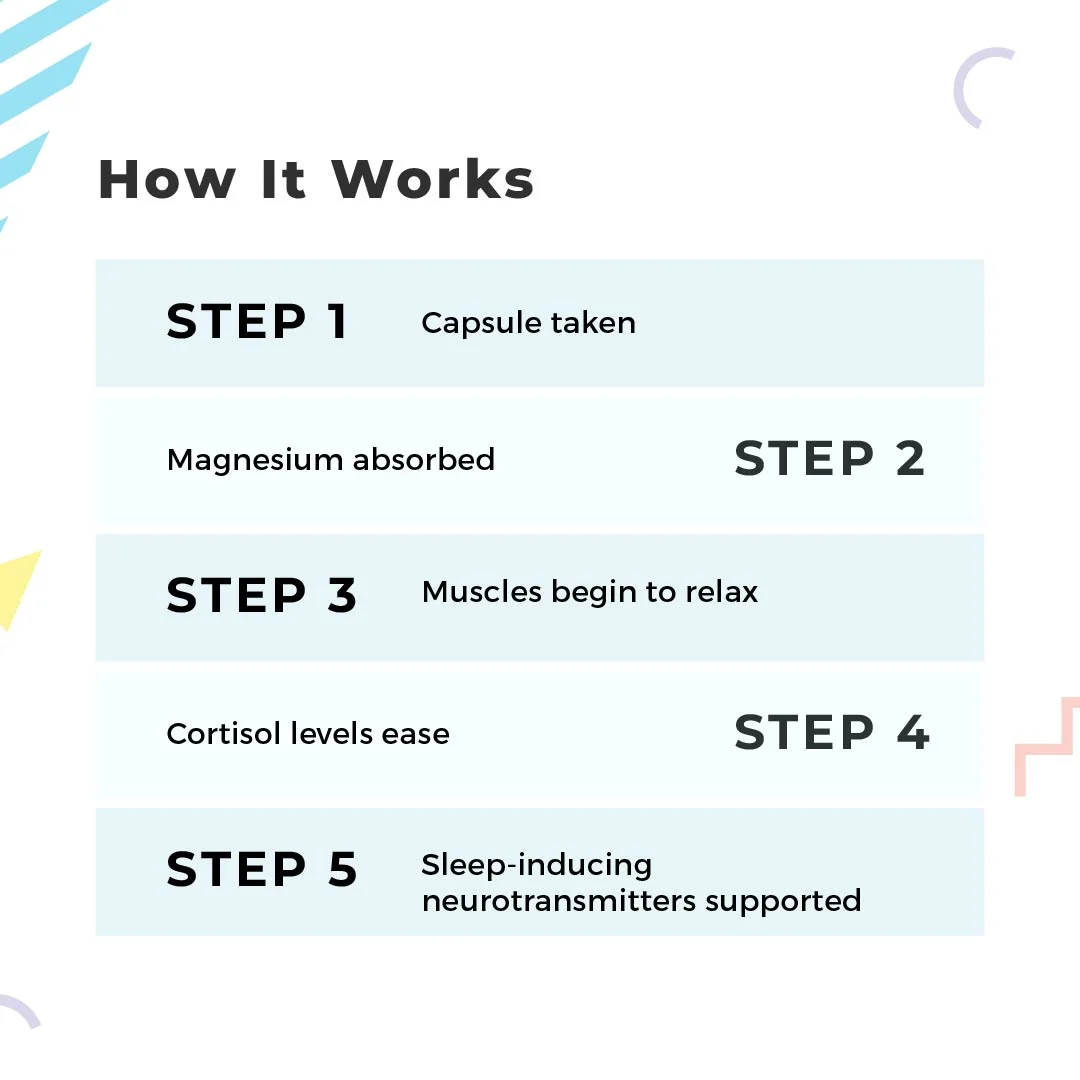

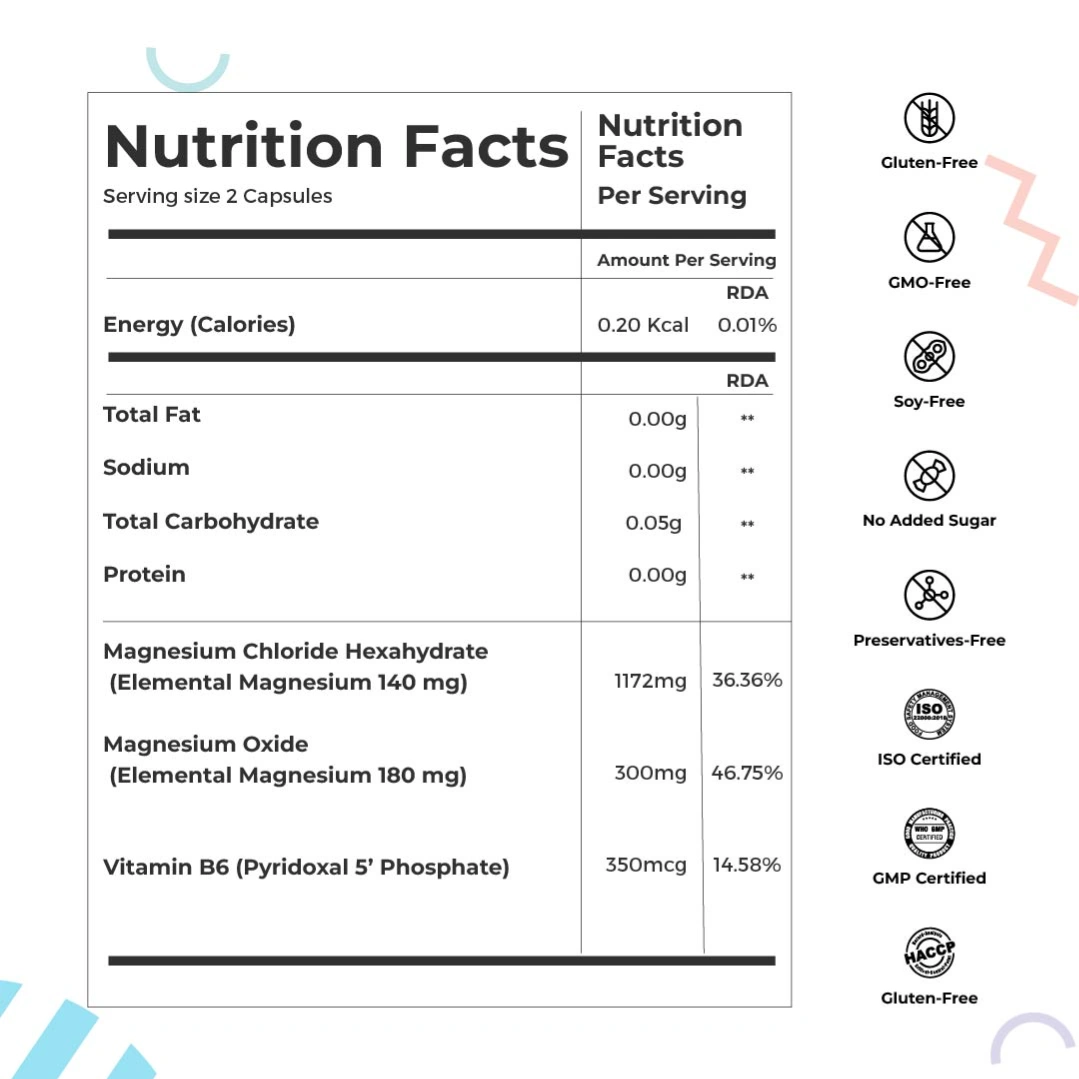








Magni-Strength – Daily Calm, Deep Sleep, Strong Heart
0
Shipping is calculated at checkout
